Refactoring¶
In general, refactoring is a technique for improving the design of existing software code without changing the way it functions.
In CODESYS, refactoring provides functions for renaming objects and variables and updating referenced pins. You can display all occurrences of renamed objects and variables and then rename them all at once or individually. In , you can also configure where CODESYS will prompt you for refactoring.
Renaming global variables
Requirement: A project is open with at least one function block (FB) and one global variable list (GVL). The global variable list is open in its editor and contains a variable declaration (for example, iglob1). FB uses iglob1.
Select the global variable name
iglob1.Right-click the variable and click .
In the Rename dialog box, type a name in the New name input field, for example
iglobNeu, and click OK.- ⇒
The Refactoring dialog box opens. In the device tree view on the left, the GVL and FB objects are highlighted in red and yellow. In the view on the right, FB in is open in its editor and
iblob1has already been renamed asiglobNeu.
Click OK.
- ⇒
The
iglob1global variable is now namediglobNeuacross your project.
Select the global variable name
iglob1.Right-click the variable and click .
In the Rename dialog box, type a name in the New name input field, for example
iglobNeu, and click OK.- ⇒
The Refactoring dialog box opens. In the device tree view on the left, the GVL and FB objects are highlighted in red and yellow. In the view on the right, FB in is open in its editor and
iblob1has already been renamed asiglobNeu.
Right-click in the view on the right.
Click Reject this object and click OK.
- ⇒
The global variable (
iglob1) is not renamed asiglobNeuin FB. In all other objects in the project, the variable is renamed asiglobNeu.An error message in the messages view reports that the
iglob1identifier is not defined.
See also
Adding and removing input variables
In the declaration section of blocks, you can add and delete input and output variables by using the refactoring commands. CODESYS performs updates at the occurrence locations and calling locations of the blocks. You can accept or reject these updates individually. The Refactoring dialog box also opens for this purpose.
Requirement: The FCT (function type) POU is open in the editor. The function already contains the input variables input1, input2, and inputx. They are called in the PLC_PRG and POU programs.
Set the focus in the declaration section of the FCT function.
Click .
- ⇒
The default dialog box opens for declaring variables.
Declare the variable
input_3with the scope ofVAR_INPUTand data typeINT. Click OK to close the dialog box.- ⇒
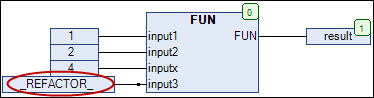
The Refactoring dialog box opens (see figure below). The affected locations are marked in yellow. (1)+(2)
In the upper right corner, select Add inputs with placeholder text from the drop-down list. (3).
In the left side of the window, click one of the highlighted objects (for example,
PLC_PRG). Right-click and choose the Accept whole project command to add the new variable at the new location of use inFCTfor the entire project.- ⇒
In the right side of the window, the change is accepted in the implementation section of
PLC_PRG: The_REFACTOR_placeholder appears at the location where the new variable was inserted.
Click OK to close the Refactoring dialog box.
Click . Search the project for “_REFACTOR_” to check and edit the affected locations.
Please note: As an alternative, you can insert the new variable with another initialization value without working with a placeholder first. In this case, in Step 4 you select “Add inputs with the following value” and type the value in the field on the right side of the drop-down list.
Example of a new variable with placeholder text in a CFC block:
Please note that you can also remove variables with refactoring.
See also
Reordering variables in the declaration
In the declaration part of function blocks, you can change the order of declarations by refactoring This is possible for declarations with scope VAR_INPUT, VAR_OUTPUT, or VAR_IN_OUT.
Requirement: The declaration part of a POU is open and includes declarations, for example:
VAR_INPUT
invar2 : INT;
invar1 : INT;
in : DUT;
bvar : BOOL;
invar3 : INT;
Right-click in this declaration block to access the context menu.
Click .
- ⇒
The Reorder dialog box opens with a list of
VAR_INPUTvariables.
Drag the invar1 : INT; entry to the position before the invar2. entry.
- ⇒
The
invar1declaration is now at the top position.
Click OK to close the dialog box.
- ⇒
The Refactoring dialog box opens. The affected locations are marked in yellow (see figure above).
Click OK to accept the new order for the function block.