Visualization Element ‘Scrollbar’¶
Symbol: 
Tag: Common controls
This element sets the value of a variable, depending on the position of the scrollbar.
Element properties
| Element name | Optional Tip: Assign individual names for elements so that they are found faster in the element list. Example: |
| Element type | Scrollbar |
| Value | IEC variable as type integer that includes the position of the scroll box in the scroll bar. |
| Minimum value | Least value of the scrollbar (fixed value or variable). |
| Maximum value | Greatest value of the scrollbar (fixed value or variable). |
| Page size | Page size
Requirement: Visible when the Move to click property is not selected. |
| Move to click | Function of the scrollbar at visualization runtime when it is clicked:
|
Element property ‘Position’
The position defines the location and size of the element in the visualization window. These are based on the Cartesian coordinate system. The origin is located at the upper left corner of the window. The positive horizontal x-axis runs to the right. The positive vertical y-axis runs downwards.
| X | X coordinate of the upper left corner of the element Specified in pixels. Example: |
| Y | Y coordinate of the upper left corner of the element Specified in pixels. Example: |
| Width | Specified in pixels. Example: |
| Height | Specified in pixels. Example: |
Note
You can also change the values by dragging the box symbols (  ) to other positions in the editor.
) to other positions in the editor.
See also
Element property ‘Bar’
The property defines the representation of scaling and direction of travel.
| Orientation | Alignment of the slider; defined by the ratio of width to height.
You can modify the alignment in the visualization editor by using the pointing device to adjust the width and height of the scrollbar. |
| Running direction | The drop-down list varies depending on the alignment of the slider. Horizontal
Vertical
|
Element property ‘Colors’
The properties contain fixed values for setting colors.
| Color | Color for the element in its normal state. Please note that the normal state is in effect if the expression in the property is not defined or it has the value |
| Alarm color | Color for the element in alarm state. Please note that the alarm state is in effect if the expression in the property has the value |
| Transparency | Value (0 to 255) for defining the transparency of the selected color. Example |
See also
Element property ‘Texts’
The properties contains character strings for labeling the element. The character string can also contain a placeholder with a format definition. In runtime mode, the placeholder is replaced by the current value in the specified format.
CODESYS accepts the specified texts automatically into the GlobalTextList text list. Therefore, these texts can be localized.
| Text | Character string (without single straight quotation marks) for the labeling the element. Example: The variable that contains the current value for the placeholder is specified in the property . |
| Tooltip | Character string (without single straight quotation marks) that is displayed as the tooltip of an element. Example: The variable that contains the current value for the placeholder is specified in the property . |
See also
- <no title>
- Designing Visualizations with Elements
- Placeholders with Format Definition in the Output Text
Element property ‘Text properties’
The properties contain fixed values for the text properties.
| Horizontal alignment | Horizontal alignment of the text within the element. |
| Vertical alignment | Vertical alignment of the text within the element. |
| Font | Example: Default
|
| Font color | Example: Black
|
| Transparency | Whole number (value range from Example:
Please note: If the color is a style color and already has a transparency value, then this property is write-protected. |
Element property ‘Text variables’
These properties are variables with contents that replace a format definition.
| Text variable | Variable (data type compliant with the format definition). It contains what is printed instead of the format definition. Example: Note: The format definition is part of the text in the property . Note: If you specify a variable of type enumeration with text list support, then the name of the enumeration data type is added automatically in angle brackets after the variable name. Example: |
| Tooltip variable | Variable (data type compliant with the format definition). It contains what is printed instead of the format definition. Example: Note: The format definition is part of the text in the property . |
See also
Element property ‘Dynamic texts’
The properties contain references to the texts of a text list.
| Text list | Variable (string) or name of the text list as a fixed string in single straight quotation marks. Example:
|
| Text index | Text list ID. This refers to the desired output text.
|
| Tooltip index | Text list ID. This refers to the desired output text.
|
See also
- Text list: Textlist
Element property ‘Font variables’
The variables allow for dynamic control of the text display.
| Font name | Variable ( Example: The selection of fonts corresponds to the default Font dialog box. |
| Size | Variable (numeric data type). Contains the font size (in pixels or points). The applied unit is specified in brackets after the variable name.
Tip: The font size is specified in points (example: Arial 12). Use points when the variable font size should match a font, for example if a font is set in the property . |
| Flags | Variable ( Flags:
Note: You can combine the font displays by adding the coding of the flags. For example, a bold and underlined text: |
| character set | Variable ( The selection of character set numbers corresponds to the Script setting of the standard Font dialog box. |
| Color | Variable ( Example: |
| Flags for text alignment | Variable (integer data type). Contains the coding for text alignment. Example: Coding:
Note: You can combine the text alignments by adding the coding of the flags. For example, a vertical and horizontal centered text: |
Note
Fixed values for displaying texts are set in Text properties.
See also
Element properties ‘Color variables’
The properties contains variables for dynamically controlling variables.
| Toggle color | Dynamic control of toggle color
|
| Normal state | The normal state is in effect if the variable in is not defined or it has the value FALSE. |
| Frame color | Variable (DWORD) for the frame color Example: |
| Fill color | Variable (DWORD) for the fill color Example: |
| Alarm state | The alarm state is in effect if the variable in has the value TRUE. |
See also
Element property ‘State variables’
The variables control the element behavior dynamically.
| Invisible | Variable (
|
| Deactivate inputs | Variable (
|
See also
 ) opens the input assistance.
) opens the input assistance. : The scrollbar moves to the clicked position.
: The scrollbar moves to the clicked position. : The scrollbar moves to one
: The scrollbar moves to one  : The
: The  : Drop-down list with style fonts.
: Drop-down list with style fonts.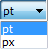 : If you click in the value field, a drop-down list opens on the right for setting the unit.
: If you click in the value field, a drop-down list opens on the right for setting the unit. symbol appears in the value field.
symbol appears in the value field.